Sowing comparison for barley
To sum up, it can be stated that the direct sowing of barley generates identical yields to those obtained in mulch sowing. However, extensive direct sowing leads to higher weed pressure, especially in the case of grasses.
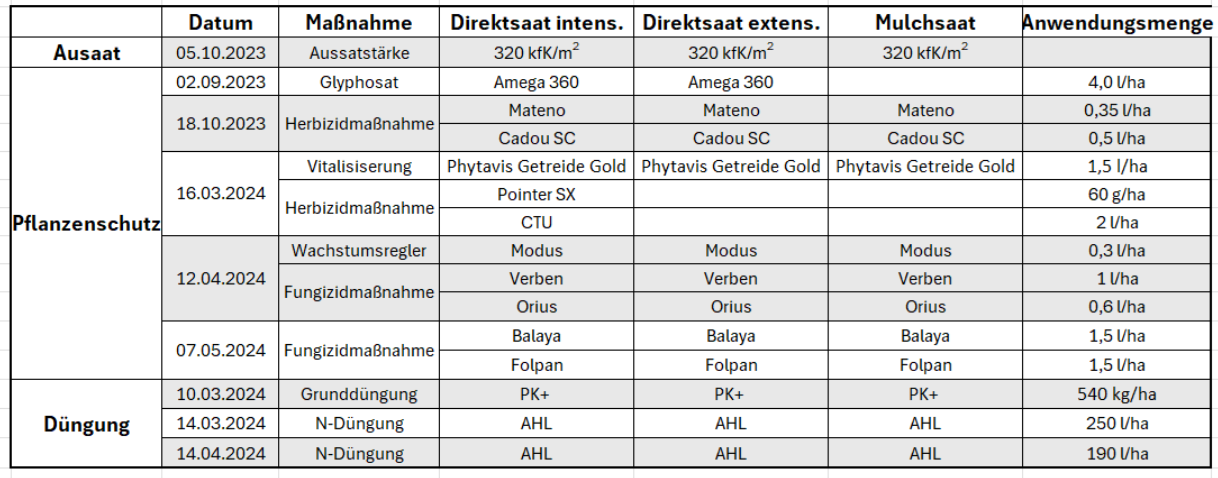
We compared direct sowing with conventional mulch sowing with winter barley (winter rape as preceding crop) at the Wambergen site in the cultivation year 2023/24. Furthermore, we tested whether and how two different plant protection strategies (intensive/extensive) have an effect in direct sowing, whereas an extensive strategy was chosen for mulch sowing.
Trial procedure
The sections were prepared for direct sowing with a glyphosate treatment (UX5201 Super) at the beginning of September. The Catros+ 5000-2 Pro and the Cenius 3002 Special were used to prepare the area scheduled for mulch sowing.
The winter barley (KWS Exquis) was sown with a sowing rate of 320 seeds/m² on all part-areas at the beginning of October. Direct sowing was carried out with the Primera DMC 3000-C (18.75 cm row width) and mulch sowing with the Centaya 3000 Super + rotary cultivator (12.5 cm row width).
We carried out a herbicide application for weed control on all part-areas in the middle of October. A second herbicide application was carried out only on the intensive direct sowing section in mid-March. The additional crop protection applications as well as fertilisation (ZA-V 4200 & UF 2002 with FT1001) were carried out uniformly in all variants (see overview).
What was the focus of our investigations?
Firstly, what interested us in this trial was whether the same plant protection strategy is possible for direct sowing as for mulch sowing. Furthermore, we wanted to know whether barley achieves an identical yield level in direct sowing as in mulch sowing and whether a business benefit generally arises from direct sowing. Finally, we also considered whether direct sowing has an effect on the soil structure.
What happened in the field?
It should be noted that the entire growing season was characterised by very high precipitation.
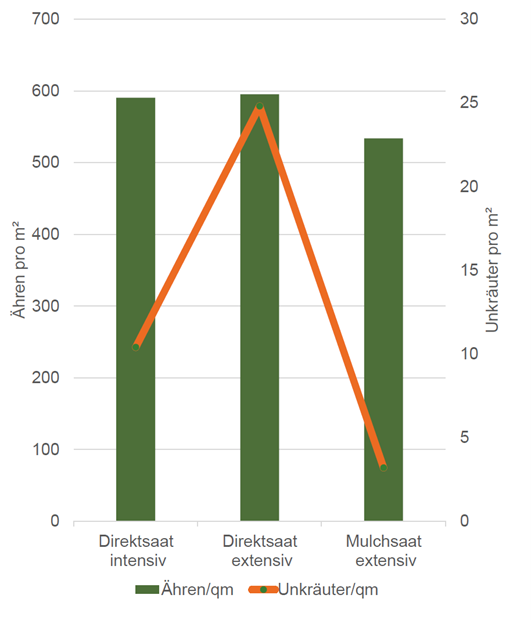
The plant densities were at a high level in all three variants (see graphic). The row width obviously played a role in this respect. Differences were observed with respect to weed pressure. Here the subsequent crop closure had an effect in the direct sowing variants as a result of the higher row width. In particular, extensive direct sowing struggled with higher weed pressure, whereby intensive direct sowing clearly benefited from the herbicide application in the spring; the weed pressure could be halved here.
Basically it can be said that there are only a few agents which can be used against grasses in barley, and the success of the treatment also leaves much to be desired at only approx. 50 %.
What about the yield?
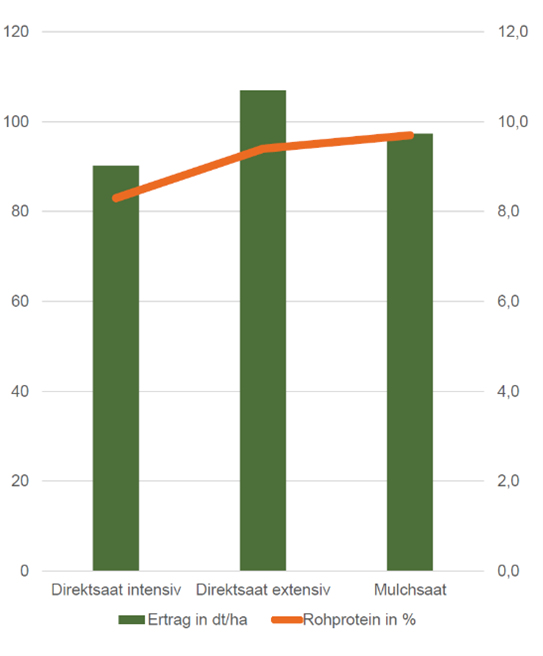
With respect to yield, all variants reached a very high level for our region. Oil seed rape as a preceding crop is ideal for direct sowing. Extensive direct sowing generated the highest yield. This shows that the grass measure in the intensive direct sowing variant in spring cost approx. 15dt/ha of yield.
The crop in mulch sowing was always somewhat more advanced than the crop in direct sowing over the entire growing period. By harvesting time, the barley was more broken down and therefore more difficult to harvest. This led to higher harvest losses from volunteer grain. A somewhat earlier harvest date would have been appropriate here, as well as more intensive treatment with growth regulator/fungicide against eyespot.
The moisture level in the complete crop was low at approx. 11 %.
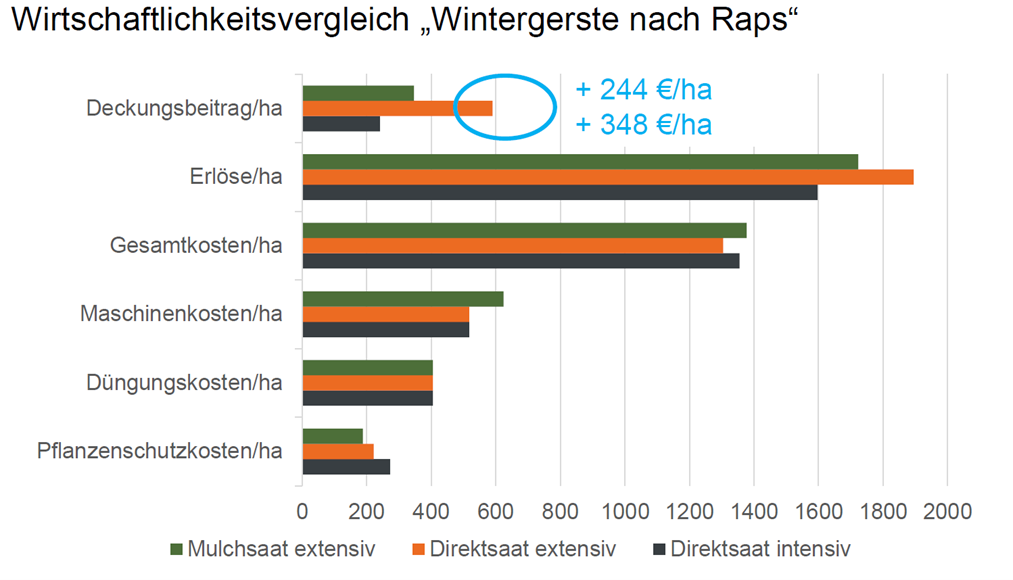
The higher plant protection costs and the lower yield in intensive direct sowing made themselves felt in the net profit. This is significantly below the result of the other two variants with respect to the contribution margin. Extensive direct sowing performed best of all here. The higher weed pressure is not reflected in the good result.
Conclusion: We obtained a very good yield and were able to cut costs through direct sowing. Direct sowing has not had an effect on the soil structure so far. However, the changeover to direct sowing did not take place on the area until the barley had been sown. We are interested in the medium-term development here, which is why we will work with direct sowing over several consecutive years. In future, it will be closely monitored how the weed dynamics change with direct sowing. After the winter barley was harvested, the straw was left on the area and a catch crop sown, whereby the tine coulter of the Primera DMC 3000-C enabled the catch crop to establish itself very well. Maize will be grown in the cultivation year 2024/25 and various soil tillage intensities compared.